Are Private Investigators Legal in the UK? Find Out Now
- Sentry Private Investigators
- May 17, 2025
- 14 min read
Updated: Jul 28, 2025
The Legal Reality of Private Investigation in the UK

Are private investigators legal in the UK? The simple answer is yes, but the reality is much more complicated. The UK's private investigation industry operates within a unique legal framework. It's defined more by what isn't specifically forbidden than by strict rules and regulations. This means understanding the legal boundaries is essential for both investigators and potential clients. This absence of formal licensing creates a distinctive operational landscape.
For over two centuries, the private investigation sector in the UK has operated without formal licensing, leaving it largely unregulated. This lack of oversight has led to concerns about unethical practices, invasions of privacy, and insufficient data protection. These concerns have, in turn, fuelled calls for increased regulation. Despite this, the industry remains vital, with private investigators playing key roles in legal, corporate, and personal matters. To learn more about the ongoing discussion surrounding PI regulation, you can find additional information from the Law Society. This long history without licensing has undoubtedly shaped the industry's current structure, impacting how investigators operate and interact with their clients. However, this doesn't mean the industry functions in a complete legal void.
Key Legislation Guiding Private Investigators
Although no single law governs the entire private investigation profession, several key pieces of legislation influence acceptable practices. These laws establish a vital structure for understanding what actions are permissible and what actions cross the line into illegal activity.
For instance, the Data Protection Act 2018 and the UK GDPR strictly control how personal data is gathered, stored, and utilised. These regulations place substantial restrictions on the activities of investigators. Further legal boundaries exist to protect individuals and ensure responsible practices.
Additionally, legislation like the Protection from Harassment Act 1997 prohibits investigators from engaging in harassing or intimidating behaviour. The Regulation of Investigatory Powers Act 2000 (RIPA) governs surveillance activities, defining what type of surveillance is legal and under what specific circumstances. This complex legal web necessitates careful navigation by investigators to maintain ethical and legal operations, even without specific licensing.
The Role of Professional Bodies
Without official licensing, professional organisations play a significant role in upholding best practices and ethical standards within the private investigation industry. Groups like the Association of British Investigators and the World Association of Detectives offer guidance, training, and accreditation for investigators. This provides a measure of reassurance for clients looking for trustworthy professionals.
These bodies strive to maintain professional standards and ensure members operate within legal boundaries. For example, many professional organisations encourage adherence to the Information Commissioner's Office (ICO) guidance on data protection for private investigators. This emphasis on data protection highlights the growing importance of privacy in today's investigations. This focus on professional standards and ethical conduct is paramount in an industry still awaiting formal licensing.
What PIs Can Legally Do: Capabilities and Limitations
Beyond Hollywood's often-exaggerated portrayal of private investigators, real-world PIs in the UK operate within clearly defined legal boundaries. This section clarifies the actual capabilities and limitations of these professionals, giving you a clearer picture of what to expect when engaging their services.
Legitimate Investigative Techniques
Ethical private investigators employ a range of legal techniques to gather information. Surveillance, when conducted legally and ethically, is a standard practice. This involves observing subjects in public areas without trespassing or invading their privacy. The goal might be to document activities, interactions, or movements relevant to a case. For instance, a PI might observe a subject's behaviour in public to gather evidence related to a suspected infidelity case.
Background checks are another essential tool. These checks provide legal access to publicly available information, revealing details such as employment history, addresses, and any criminal records. Importantly, PIs cannot access private data like medical records or bank account details without proper legal authorisation. This safeguards individual privacy and ensures the investigation remains within legal limits.
Digital Investigations: Navigating the Legal Landscape
Digital investigations are increasingly important in today's world. PIs can legally examine publicly accessible online information, including social media profiles and websites. However, hacking or unauthorised access to private accounts is strictly prohibited. This crucial distinction underscores ethical and legal practices in the digital realm.
Understanding the legal framework for private investigators is vital. Individuals in the US facing legal challenges can explore resources such as legal help for veterans. Additionally, staying informed on ethical data handling is crucial. It ensures your chosen PI operates responsibly and respects privacy laws.
Admissible Evidence vs. Compromising Tactics
It’s important to recognise that not all investigative methods yield evidence admissible in court. While legally gathered information can be valuable, some tactics could jeopardise a case if employed improperly. Illegally obtained recordings, for instance, might be inadmissible. Choosing a PI who understands these nuances is therefore essential.
This means selecting an investigator who prioritises legal compliance and gathers evidence ethically. This approach safeguards your interests and strengthens your case, ensuring the investigation stays within legal bounds and maximising the usability of any evidence obtained.
Real-World Scenarios: Legal and Ethical Practices
Skilled private investigators understand the balance between acquiring information and respecting legal limits. In a corporate fraud investigation, for example, a PI might legally review company records and conduct interviews to uncover evidence. They would not, however, engage in illegal activity such as hacking employee emails.
This commitment to ethical practices ensures the investigation is conducted legally and the evidence gathered is credible. It also protects both the PI and the client from legal ramifications. This demonstrates professionalism and integrity.
By understanding the legal framework within which private investigators operate, you can make informed decisions and choose a professional who adheres to the highest ethical and legal standards. This knowledge empowers you to achieve your investigative goals legally and effectively.
Red Lines: When Investigation Becomes Illegal

While private investigators are legal in the UK, the industry's lack of comprehensive regulation can blur the lines between legal investigation and illegal activity. Understanding these boundaries is crucial for anyone considering hiring a PI. Reputable investigators understand these limitations and operate strictly within the law.
Illegal Surveillance: Trespassing and Privacy Violations
One key area where investigations can cross the line is surveillance. Observing someone in public is generally legal. However, trespassing onto private property to conduct surveillance is not. This includes entering someone's home, garden, or business premises without permission.
Another significant legal issue involves the use of covert listening devices, or bugging. Bugging someone's property without consent is a serious offence under the Regulation of Investigatory Powers Act 2000 (RIPA). Penalties for these violations can be severe, including criminal charges.
For example, planting a hidden camera on someone's car to track their movements without a legitimate interest is illegal surveillance. This action breaches privacy laws and undermines legal investigative practices unless the tracking device is used as an aid to surveillance.
Data Protection Laws: Handling Information Legally
The Data Protection Act 2018 and the UK GDPR place strict limits on how private investigators obtain and use personal data. Accessing someone's bank records, medical files, or private communications without proper legal authority is illegal. Investigators must have a lawful basis for processing data. This might include explicit consent from the individual or a legitimate legal requirement.
Even seemingly harmless actions, like accessing someone's social media accounts without their knowledge, could be illegal if done without proper justification. This highlights the importance of hiring a data-conscious PI.
Recognising Red Flags: Client Requests and Investigator Promises
Certain client requests should raise immediate red flags. Asking a PI to hack into someone's email account or obtain confidential information through illegal means is a clear warning sign. The client is seeking illegal services. If a PI promises outcomes that seem impossible to achieve legally, they might be willing to cross legal boundaries.
This could include guaranteeing access to restricted information or promising improbable results given legal constraints. These scenarios demonstrate the importance of ethical considerations when hiring a PI. Be wary of investigators making unrealistic promises. Their desire to secure your business might outweigh their commitment to legality.
Consequences of Illegal Activity: Protecting Yourself and Your Case
Engaging a PI who conducts illegal activities puts both the investigator and the client at risk. Illegally obtained evidence is usually inadmissible in court. It can't be used to support your case. Furthermore, involvement in illegal investigative practices could result in legal repercussions for you.
This underscores the importance of due diligence when selecting an investigator. Ensure they demonstrate a clear understanding of, and commitment to, legal boundaries. By prioritising lawful methods, both you and your investigator remain protected. This commitment to legality not only safeguards you but also reinforces the integrity of your case.
Inside the UK's Private Investigation Industry
The UK's private investigation sector operates with a distinct air of secrecy. Thousands of professionals work in this field, often out of the public eye. But just how big is this industry, and how does it function with limited regulation? This section provides a look into this often-hidden world, examining its size, the challenges it faces, and the ongoing efforts to raise professional standards.
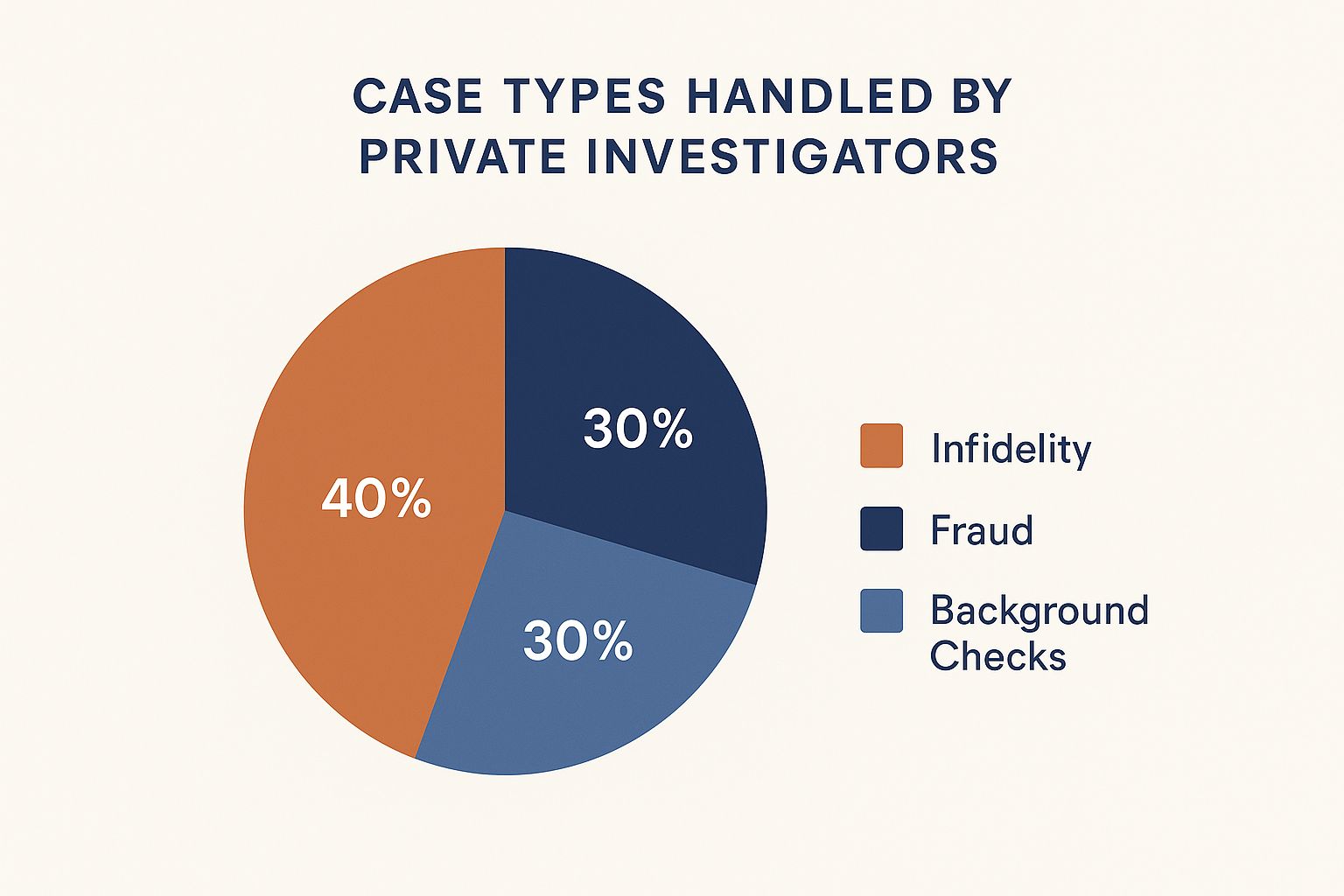
The infographic above shows the typical breakdown of cases handled by private investigators. Infidelity investigations make up 40% of the workload. Fraud and background checks each account for 30%. This data highlights the varied nature of private investigation work and the considerable demand for services related to both relationship and financial issues.
The Scale of the Industry: Counting the Numbers
Pinpointing the exact number of private investigators in the UK is tricky due to the absence of a centralised licensing system. Industry estimates suggest there are between 10,000 and 15,000 active private investigators nationwide, including both agency employees and self-employed individuals. You can find more information on these figures at Find a Detective. This substantial figure underscores the industry's scale and the difficulties in maintaining consistent standards and accountability.
Voluntary Regulation: Raising the Bar
Without mandatory licensing, professional organisations like the Association of British Investigators and the World Association of Detectives are key to upholding ethical standards and promoting best practices. These organisations offer training, accreditation, and support to investigators, fostering professionalism and accountability within the field. This voluntary regulation aims to improve the quality of services and build client trust.
The DPA Register: A Partial View
While not all private investigators are registered, the Data Protection Act (DPA) register provides a snapshot of part of the industry. Currently, only around 1,626 investigators are listed on the public DPA register. This significant difference between the estimated number of investigators and those registered highlights the need for broader registration and regulation. This discrepancy also underlines the potential risks clients take when hiring an investigator who may not be following data protection rules.
To further illustrate the distribution of Private Investigators across the UK, the table below provides a breakdown of their concentration in major cities. This helps to visualise the regional variations within the industry.
Distribution of Private Investigators Across the UK Regional concentration of private investigators in major UK cities
City | Estimated Number of PIs | Percentage of UK Total |
|---|---|---|
London | 4,000 | 40% |
Birmingham | 1,000 | 10% |
Manchester | 750 | 7.5% |
Leeds | 500 | 5% |
Glasgow | 500 | 5% |
Other | 3,250 | 32.5% |
Note: These figures are estimates based on industry data and may not reflect the exact number of PIs. |
As the table shows, London has the highest concentration of private investigators, followed by Birmingham and Manchester. The remaining percentage is spread across other UK cities and towns. This distribution reflects the population density and economic activity in these areas, which often correlates with demand for investigative services.
Accountability and the Future of Regulation
The large number of unregistered investigators raises serious questions about accountability and quality control within the industry. For clients, this means careful research and selecting an investigator registered with a reputable professional body is crucial. Further discussions and potential government action regarding licensing and regulation within the UK's private investigation sector are likely in the future.
Navigating Privacy and Data Protection Boundaries

In the private investigation field, information is paramount. However, accessing and using this information, particularly personal data, is heavily regulated in the UK. Understanding data protection is crucial for both private investigators and their clients. Operating outside these boundaries is illegal. This section will explore the vital role of data protection in legitimate private investigation.
GDPR and the Data Protection Act: Reshaping Investigative Practices
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Data Protection Act 2018 have significantly impacted UK private investigation practices. These regulations establish strict rules for collecting, processing, and storing personal data. Private investigators must operate within these parameters for legal compliance.
For example, investigators need a lawful basis for processing personal data. These lawful bases might include obtaining explicit consent from the individual or demonstrating a legitimate interest that doesn't override the individual's rights. This ensures investigations are conducted ethically and responsibly, respecting individual privacy. This focus on data protection emphasises transparency and accountability.
Data Subject Rights: Impact on Investigations
Data subjects, the individuals whose data is being processed, have specific rights under the GDPR. These include the right to access their data, the right to rectify inaccurate data, and the right to erasure (the “right to be forgotten”). These rights influence how investigators work.
A subject, for instance, can request access to the data collected about them. Investigators must be prepared to provide this information and explain its use. This transparency keeps individuals informed and in control of their personal information.
Compliance and Reputable PIs
Reputable private investigators prioritise data protection and invest in compliance. They implement strict data protection policies and procedures for handling personal information legally and ethically. This includes staff training, secure data storage, and regular practice reviews.
A new data protection code of conduct for UK private investigators, launched in November 2024, provides further guidance for responsible data handling. Learn more about this new code of conduct. This voluntary code reinforces the industry's commitment to ethical data practices and client reassurance.
Recognising Data-Conscious Investigators
Clients should look for key indicators when choosing a private investigator. Transparency regarding data handling is vital. A reputable investigator will explain their compliance with data protection laws. They should also have clear procedures for data subject access requests. These factors signify a professional and trustworthy service. Prioritising these practices helps you choose an investigator who operates legally and ethically, protecting your interests and individual privacy.
Finding a Legitimate PI: Your Step-by-Step Guide
Hiring a private investigator (PI) can feel overwhelming. The UK industry isn't regulated, making choosing the right PI even more critical. A good PI helps you achieve your investigative goals legally and ethically. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to finding a legitimate, qualified professional.
Essential Questions to Ask a Potential PI
Asking the right questions reveals a PI's commitment to legal compliance and ethical practices. Consider these crucial questions:
"How do you ensure compliance with data protection laws, like GDPR?" A competent PI should easily explain their data handling procedures and adherence to the GDPR.
"Can you provide examples of similar cases you've handled successfully?" While maintaining confidentiality, they should discuss relevant experience.
"What professional organisations do you belong to?" Membership in reputable organisations, such as the Association of British Investigators (ABI), demonstrates professionalism.
"What is your process, and do you guarantee results?" Beware of guaranteed outcomes. This could suggest a willingness to cross legal boundaries.
Red Flags to Watch Out For
Recognising warning signs protects you from legal issues and financial loss. Watch out for these red flags:
Guaranteed results or access to restricted information. These promises often indicate illegal activity.
Reluctance to discuss data protection or affiliations. This lack of transparency suggests a potential disregard for ethical conduct.
Pressure for quick decisions or upfront payment without a contract. Take your time and vet potential PIs thoroughly.
Ethically questionable or potentially illegal methods. Trust your instincts. If something feels wrong, it probably is.
Documentation and Agreements: Protecting Your Interests
A legitimate PI provides clear, comprehensive documentation.
A detailed contract outlining the scope of work, fees, and payment terms. This protects both parties.
Confirmation of professional indemnity insurance. This safeguards you against financial losses due to negligence or misconduct.
Clear communication, including regular updates and reports. Open communication indicates professionalism and accountability.
Evaluating Credentials: Beyond the Basics
While licensing isn't mandatory for UK PIs, some qualifications indicate professionalism.
Membership in respected professional organisations: This demonstrates adherence to industry standards and ethical conduct.
Data Protection Act (DPA) registration: While not always mandatory, DPA registration shows compliance with data protection laws.
Relevant experience and specialisations: Choose a PI with experience in your specific type of investigation.
Before hiring a PI, review the checklist below summarising essential verification criteria. It provides a helpful overview of what to look for and how to confirm a PI's legitimacy.
Checklist for Hiring a Legal Private Investigator
Essential criteria to verify when selecting a private investigator in the UK
Verification Criteria | Importance | How to Check |
|---|---|---|
Data Protection Compliance | Protects your privacy and ensures legal operation. | Ask about GDPR compliance and data handling policies. |
Professional Affiliations | Indicates commitment to industry standards. | Inquire about memberships in reputable organisations like the ABI. |
Experience and Expertise | Ensures competence in your specific case type. | Discuss relevant case examples and specialisations. |
Insurance and Contracts | Protects you from financial risk and clarifies agreements. | Verify professional indemnity insurance and review contracts thoroughly. |
Transparent Communication | Promotes accountability and keeps you informed. | Expect regular updates and clear explanations of the investigation process. |
By following this guide and using the checklist, you can confidently find a legitimate PI in the UK. Choosing a qualified and ethical PI is crucial for a successful investigation. They will work ethically and legally, protecting your interests and achieving your objectives.
The Future of Private Investigation Regulation
The UK's private investigation industry currently operates with minimal regulation. Discussions around potential changes, however, are gaining traction. Key concerns driving this momentum include data protection, ethical conduct, and the need for greater accountability within the industry. This section explores the potential future of regulation for private investigators in the UK and its implications for both investigators and their clients.
Potential Licensing Systems and Their Impact
One likely development is the implementation of a formal licensing system for private investigators. This could involve establishing a regulatory body tasked with setting industry standards, issuing licenses, and handling complaints. Such a system could significantly reshape the industry, creating a clearer distinction between legitimate professionals and unqualified operators. This increased oversight could boost public trust and confidence in the profession.
A formal licensing system could also introduce minimum qualification requirements, potentially encompassing training, experience, and background checks. This would raise the bar for entry, ensuring a baseline level of competence. However, these changes might also lead to increased costs for investigators, potentially resulting in higher fees for clients.
Voluntary Certifications: Current Status and Future Role
In the current absence of mandatory licensing, voluntary certifications offer a degree of quality assurance. Organisations like the Association of British Investigators (ABI) and the World Association of Detectives provide certifications based on experience, training, and ethical commitments. These credentials signal a commitment to best practices, offering clients some reassurance when selecting an investigator.
In the future, voluntary certifications could complement formal licensing. They might demonstrate specialisations or advanced training beyond basic licensing requirements, allowing investigators to differentiate themselves. This would create a tiered system, providing clients with greater choice and transparency when selecting an investigator based on their specific needs. When looking for a legitimate investigator, remember to check out a general home security checklist to maintain your privacy.
Major Cases and Calls for Change
High-profile cases involving unethical or illegal practices by private investigators have fuelled demands for stricter regulation. These incidents highlight the potential risks associated with the current unregulated environment and underscore the need for accountability. Such cases often serve as catalysts for legislative change, demonstrating the real-world consequences of inadequate oversight and the importance of protecting individuals from malpractice.
International Models and UK Reforms
When developing regulatory frameworks, the UK might draw inspiration from international models. Countries like the United States, Australia, and Canada have varying licensing and regulatory systems for private investigators. Examining these systems could inform UK reforms, allowing policymakers to identify best practices and adapt them to the UK context. You can learn more about this topic in our blog post categories. This comparative approach would help create a system tailored to the unique characteristics of the UK private investigation landscape.
Investigator Accountability and Client Protections
Proposed regulatory frameworks are likely to prioritise investigator accountability and client protections. Licensing systems would provide a formal mechanism for handling complaints and imposing sanctions for misconduct. This offers recourse for clients who experience unprofessional or illegal behaviour. Stronger regulations would also increase transparency, making it easier for clients to verify an investigator's credentials. This benefits both clients seeking reliable services and reputable investigators seeking to distinguish themselves from unethical operators.
The changing regulatory landscape presents both opportunities and challenges. For clients, it promises greater protection and increased confidence. For investigators, it signifies a move towards greater professionalism and recognition of their important role in various legal, corporate, and personal matters. Staying informed about these changes is crucial for navigating the current landscape and preparing for the future of private investigation in the UK. Contact Sentry Private Investigators Ltd today to discuss your investigative needs. Visit https://www.sentryprivateinvestigators.co.uk to learn more and schedule a consultation. We offer a range of legal and ethical investigative services tailored to your specific requirements. We're here to help you find the answers you need, legally and discreetly.
