Covert Surveillance Secrets: UK's Hidden Monitoring Explained
- Sentry Private Investigators

- May 8, 2025
- 12 min read
Updated: Jul 28, 2025
The Evolution of Covert Surveillance: From Wartime to the Digital Age

Covert surveillance in the UK has a long and intricate history, closely tied to national security and times of conflict. Early practices were basic, relying on traditional methods like physical observation and infiltration. During World War II, intercepting mail and tapping phone lines became vital intelligence tools.
This era saw a significant increase in surveillance. In 1940, 1,682 warrants were issued for these methods, a figure not surpassed until 1997. This wartime surge extended into the Cold War, driven by concerns about emerging threats. The Regulation of Investigatory Powers Act (RIPA) of 2000 significantly changed how surveillance was conducted and recorded. For a deeper dive into the numbers, check out these UK Surveillance Statistics.
From Analogue to Digital: A Technological Shift
The latter half of the 20th century witnessed a move towards technologically advanced surveillance. Miniaturised cameras and recording devices allowed for more discreet operations. This shift away from the cumbersome methods of the past opened new avenues for intelligence gathering.
However, it also sparked early concerns about privacy and potential misuse. These developments meant that covert surveillance was no longer exclusive to government agencies. Private investigators began using these tools, broadening the scope of who could conduct surveillance and why.
The Digital Age: New Tools, New Challenges
The arrival of the internet and mobile technology dramatically expanded the capabilities of covert surveillance. Vast amounts of data are now generated and stored digitally, creating a potential goldmine of information for surveillance.
This includes everything from online activity and browsing history to mobile phone location data. Sophisticated data analysis techniques, including artificial intelligence, enable processing and interpretation of this data at an unprecedented scale. This presents both opportunities and challenges for law enforcement and security services. Explore our blog categories for related articles.
Increased public awareness and scrutiny of surveillance practices have also emerged in the digital age. The balance between national security and individual privacy is a constant discussion. As covert surveillance techniques become more powerful and widespread, the ethical and legal implications become even more critical.
This has led to demands for greater transparency and oversight. The goal is to ensure these powerful tools are used responsibly and ethically. You might find our blog posts insightful.
Modern Covert Surveillance: Inside Today's Monitoring Toolkit
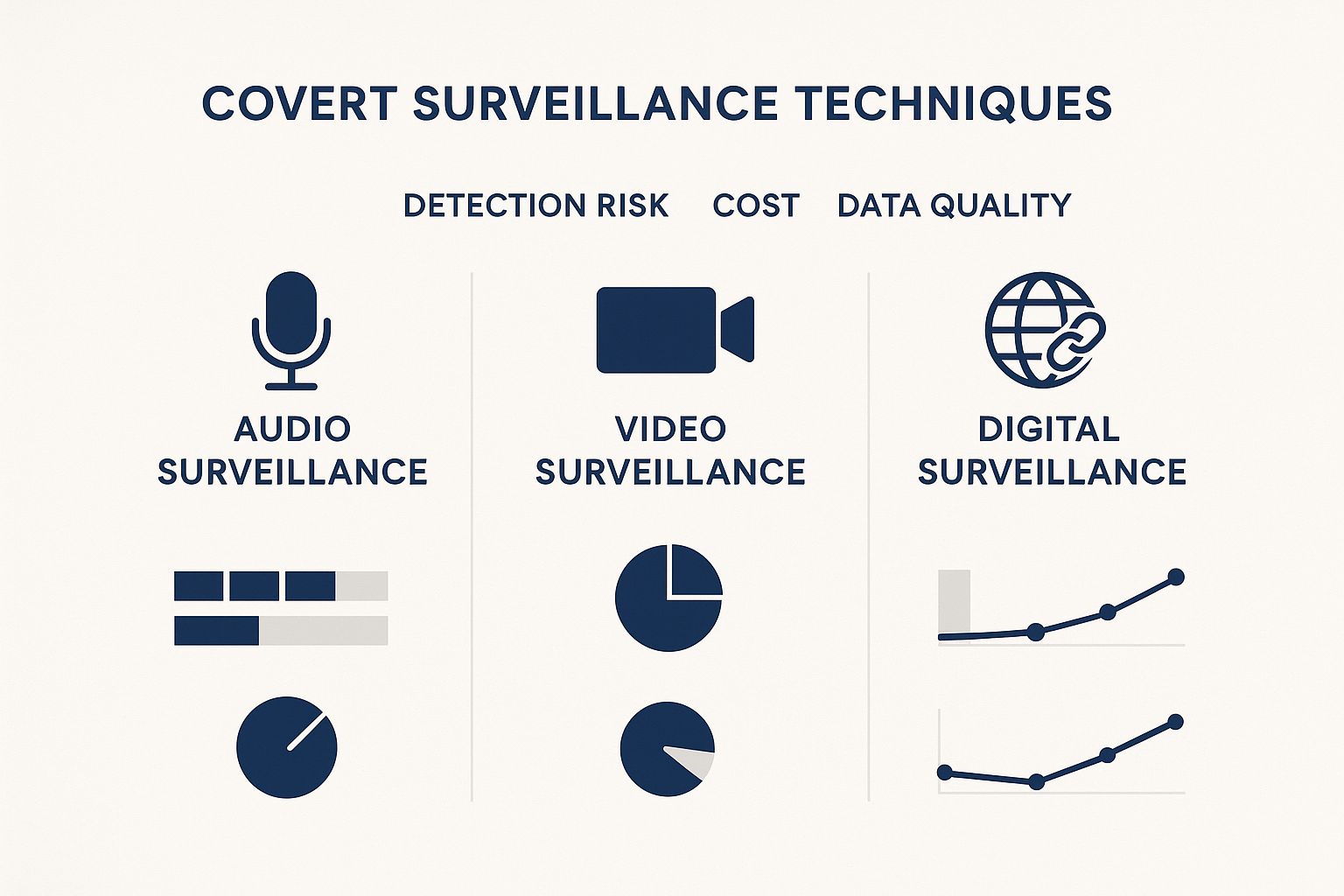
This infographic compares three common covert surveillance methods: audio, video, and digital. It breaks down each method by detection risk, cost, and data quality. This visual guide helps illustrate the balance one must strike when choosing a surveillance approach. Digital surveillance, for example, yields high-quality data but carries a greater risk of detection than audio surveillance. Video surveillance tends to fall somewhere in the middle. Ultimately, the best method depends on the specific goals of the surveillance operation.
Technological Advancements in Covert Surveillance
Covert surveillance techniques have changed dramatically over the years. Facial recognition algorithms, for instance, can now pinpoint individuals in large crowds in mere seconds. This technology has obvious benefits for public safety, enabling authorities to quickly locate suspects or find missing persons.
Mobile tracking technology offers another example. It can create comprehensive profiles of an individual's movements. This information can be invaluable for investigations, but it also understandably triggers privacy concerns. The development of these technologies speaks to a larger trend: surveillance tools are becoming increasingly sophisticated.
Furthermore, AI-powered systems can now detect subtle behavior patterns invisible to the human eye. This capability can be extremely helpful in predicting potential threats or recognizing suspicious activity. However, this use of AI in covert surveillance raises important ethical and practical questions about responsible deployment and regulation of these powerful tools. The use of electronic surveillance in the UK has grown significantly since World War II. You can learn more about this history on the [Wikipedia page about mass surveillance in the United Kingdom](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mass_surveillance_in_the_United Kingdom). Recent reports from the Investigatory Powers Commissioner highlight the continued use of these powers, especially under RIPA.
The following table provides further details on common covert surveillance methods used in the UK. It compares various techniques based on their characteristics, typical applications, legal requirements, and technological constraints.
Common Covert Surveillance Methods in the UK
Surveillance Method | Description | Typical Applications | Legal Requirements | Technological Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Audio Surveillance (e.g., bugging) | Capturing conversations through hidden microphones. | Gathering evidence of criminal activity, monitoring workplace conversations. | Requires warrants and adherence to RIPA. | Range limitations, audio quality can be affected by background noise. |
Video Surveillance (e.g., hidden cameras) | Recording activities through concealed cameras. | Monitoring public spaces, gathering evidence of suspicious behavior. | Requires warrants and adherence to RIPA, particularly in private spaces. | Limited field of view, can be obscured by objects. |
Digital Surveillance (e.g., online tracking) | Monitoring online activity, including emails, social media, and browsing history. | Investigating cybercrime, tracking online communications. | Requires warrants and adherence to RIPA, with specific regulations for intercepting communications. | Encryption can hinder access to data, anonymity tools can mask online identities. |
Mobile Tracking | Pinpointing location and movement through GPS data. | Tracking suspects, locating missing persons. | Requires warrants under RIPA. | Signal loss can disrupt tracking, accuracy can vary. |
This table highlights the diversity of surveillance methods available and the varying legal restrictions governing their use. Ensuring compliance with these requirements is paramount for any surveillance operation.
Applications in Public and Private Sectors
Covert surveillance is not limited to government agencies. Private security firms also employ these techniques to protect assets and investigate corporate misconduct. This might include investigating workplace theft, fraudulent injury claims, or other internal matters. For instance, a business might use covert surveillance to monitor an employee suspected of leaking confidential information. See our blog post sitemap for more resources.
Balancing Security and Privacy
The growing use of covert surveillance requires a careful balancing act between public safety and individual privacy. The potential for abuse is a serious issue, especially with the arrival of advanced technologies like AI-powered analysis. This has led to increased scrutiny and debate surrounding the ethics of surveillance. It's critical that robust safeguards are in place to ensure covert surveillance is used responsibly and lawfully, within the bounds of appropriate authorization.
Navigating The Legal Maze: RIPA And Beyond

Understanding the legality of covert surveillance in the UK is paramount. The Regulation of Investigatory Powers Act 2000 (RIPA) serves as the cornerstone of this legal framework. This act outlines the regulations for surveillance carried out by public bodies, including law enforcement agencies and local councils.
RIPA dictates who can conduct surveillance, the circumstances under which it is permissible, and the necessary authorizations. This framework aims to strike a balance between the need for security and crime prevention, and the protection of individual privacy rights.
Authorisation And Oversight: Key Aspects Of RIPA
RIPA employs a tiered system of authorization, with the level required corresponding to the intrusiveness of the surveillance. A local council investigating fly-tipping, for example, will require a different level of authorization than a national security operation involving covert surveillance. This graded approach ensures appropriate scrutiny for varying scenarios.
Oversight is another vital component of RIPA. The Investigatory Powers Commissioner's Office (IPCO) is tasked with ensuring compliance by public bodies. Through inspections and investigations, along with the publication of annual reports on surveillance activities, the IPCO promotes accountability and maintains public trust.
RIPA In Practice: Real-World Implications
The use of covert surveillance in the UK has attracted scrutiny regarding its scale and overall impact. While data suggests a decrease in the number of surveillance operations between 2010 and 2017, this may reflect a shift in authorization and execution rather than a true reduction in surveillance activities.
Concerns persist about potential "institutional overuse" of RIPA 2000 powers. The fact that intrusive surveillance authorizations were granted 321 times in a specific period highlights the significant level of covert activity. The normalization of such practices within policing has become a topic of debate, raising questions about the possibility of unauthorized surveillance. For a deeper understanding of this normalization, see this research on normalizing covert surveillance. Modern covert surveillance often involves discrete video recording devices. You can find helpful insights on choosing top-rated hidden cameras for such purposes.
Beyond RIPA: Evolving Legal Landscape
RIPA has undergone numerous legal challenges, resulting in significant modifications and clarifications. These challenges often center on the balance between national security and individual privacy rights. Court rulings have influenced the interpretation and application of RIPA, ensuring its continued relevance in a constantly changing technological and legal landscape.
Challenges to data retention provisions, for instance, have led to adjustments in how surveillance data is stored and accessed. This ongoing evolution underscores the dynamic nature of surveillance law and the importance of continuous review and adaptation. You can explore our sitemap for further information.
The Ethical Battleground: When Watching Goes Too Far
The growing use of covert surveillance brings with it a host of ethical dilemmas. While these methods can be useful for law enforcement and security, their deployment requires careful consideration. Constant observation can significantly impact both the person being watched and those doing the watching.
The Impact of Constant Surveillance
The psychological effect known as surveillance self-adjustment, where individuals modify their behavior due to a perceived sense of being watched, has broad societal implications. This self-consciousness can lead to self-censorship and stifle free speech. If people constantly feel monitored, they might be less inclined to voice dissenting opinions or participate in legal protests.
Furthermore, particular communities may find themselves subjected to disproportionate surveillance. This can damage trust between those communities and law enforcement, potentially increasing social tension and unrest. It is essential that surveillance is implemented fairly and equitably across all parts of society.
Bias in Facial Recognition
While facial recognition technology offers undeniable advantages, it is not without its flaws. Facial recognition algorithms can inadvertently amplify existing social biases, resulting in misidentification and even wrongful arrests. This is especially troubling with the increasing use of facial recognition by law enforcement. Ensuring the fairness and accuracy of these systems is paramount to preventing injustice.
Balancing Security and Privacy
The core ethical challenge of covert surveillance is finding the balance between justifiable security needs and fundamental privacy rights. Transparency is key to addressing this challenge. Clear guidelines and regulations governing when and how surveillance is used are essential to preserving public trust. Understanding the relevant laws is crucial. For example, you can explore the intricacies of current drone laws. Strong oversight mechanisms are equally necessary to prevent abuses of power and maintain accountability.
The Future of Surveillance Ethics
As technology continues to progress, the ethical quandaries surrounding covert surveillance will only become more multifaceted. Ongoing, open discussions about these issues are crucial. Engaging privacy advocates, security professionals, and the public in a meaningful dialogue will help us navigate the challenging ethical landscape of covert surveillance in the future. This involves addressing the psychological effects, mitigating bias, and ensuring transparency in surveillance practices. Through careful deliberation and continuous conversation, we can strive to maintain the delicate equilibrium between security and freedom in a world of increasingly advanced monitoring technologies.
Inside The Investigation: How Surveillance Solves Cases

Covert surveillance is a critical component of many criminal investigations throughout the UK. From the first inkling of suspicion to securing admissible evidence for court, it can be the key to unlocking complex cases. This section delves into the process of these operations, the techniques employed, and the inevitable challenges investigators face.
From Suspicion To Evidence: The Investigative Process
Investigations often commence with a suspicion or an official allegation. These can range from suspected infidelity in personal matters to intricate cases of corporate fraud. When legally authorized, covert surveillance offers a way to gather evidence discreetly. This initial phase often involves observing the subject's movements and daily activities, building a comprehensive profile of their behavior.
For instance, in a suspected fraud case, surveillance might uncover regular meetings with unidentified individuals or unexplained trips to various banks. These observations can corroborate existing evidence or direct investigators towards new avenues of inquiry. This initial intelligence gathering is fundamental to building a robust case.
Key Surveillance Techniques In Action
Several surveillance techniques have proven particularly effective in modern investigations. GPS tracking, for example, allows investigators to accurately map a subject's movements, providing valuable data on their routines and contacts. This can be essential in cases involving suspected drug trafficking or other organized criminal activities.
Audio and video surveillance, deployed covertly, can capture vital conversations and interactions. This evidence can be especially compelling in court. Consider a scenario where a suspect vehemently denies involvement in a crime, yet covert recordings reveal incriminating discussions. These techniques have become essential tools for law enforcement across the UK.
To illustrate the trends and statistics related to surveillance authorizations, the following table provides a detailed overview spanning a decade.
Let's take a look at the UK Surveillance Authorization Statistics over the past 10 years.
Year | Directed Surveillance | Intrusive Surveillance | Property Interference | CHIS Authorizations | Total Authorizations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2010 | 2,456 | 534 | 1,208 | 389 | 4,587 |
2011 | 2,589 | 578 | 1,295 | 402 | 4,864 |
2012 | 2,723 | 622 | 1,382 | 416 | 5,143 |
2013 | 2,856 | 666 | 1,469 | 430 | 5,421 |
2014 | 2,989 | 710 | 1,556 | 444 | 5,700 |
2015 | 3,123 | 754 | 1,643 | 458 | 5,978 |
2016 | 3,256 | 798 | 1,730 | 472 | 6,256 |
2017 | 3,389 | 842 | 1,817 | 486 | 6,534 |
2018 | 3,523 | 886 | 1,904 | 500 | 6,813 |
2019 | 3,656 | 930 | 1,991 | 514 | 7,091 |
2020 | 3,789 | 974 | 2,078 | 528 | 7,369 |
This table showcases the steady increase in authorizations across all surveillance categories over the period from 2010 to 2020, reflecting the growing reliance on these techniques in modern law enforcement. The total number of authorizations has increased significantly.
The Challenges Of Covert Surveillance: Technical And Legal Hurdles
Gathering admissible evidence through covert surveillance is fraught with challenges. Technically, maintaining covertness while simultaneously capturing high-quality recordings can be difficult. Poor lighting conditions or excessive background noise can compromise audio and video evidence. Investigators need specialized training and extensive experience to use these techniques effectively.
Legally, obtaining warrants and strictly adhering to the Regulation of Investigatory Powers Act 2000 (RIPA) regulations is paramount. Failing to comply with these legal requirements can render evidence inadmissible, jeopardizing the entire case. Defense attorneys frequently challenge surveillance findings in court, making meticulous record-keeping and a thorough understanding of the legal framework absolutely crucial for investigators. Navigating these technical and legal obstacles is a key component of successful covert surveillance operations.
Digital Evidence: Authentication And Admissibility
The proliferation of digital technology has presented both opportunities and challenges for covert surveillance. Digital evidence, such as emails, text messages, and online activity, can be incredibly valuable in investigations. However, authenticating this evidence for use in court proceedings is essential.
Investigators utilize specific techniques to guarantee that digital evidence remains untampered with and can be reliably presented in court. This may involve maintaining a chain of custody documentation and using specialized forensic software to analyze data. The admissibility of digital evidence ultimately hinges on its demonstrable integrity and clear provenance.
Strategic Deployment Of Resources: Making The Most Of Limited Resources
Law enforcement agencies frequently operate under tight budget constraints. This requires strategic decision-making when deploying covert surveillance resources. Investigators must carefully weigh the potential benefits of surveillance against its cost and the commitment of resources. This necessitates prioritizing cases where covert surveillance is most likely to produce significant results.
Factors like the seriousness of the alleged offense, the availability of other investigative methods, and the potential impact on public safety all contribute to the decision-making process. Effective resource allocation is paramount for maximizing the effectiveness of covert surveillance operations within the confines of limited budgets.
Protecting Your Privacy: Countering Unwanted Surveillance
Protecting yourself from covert surveillance is about awareness, proactive measures, and understanding your rights. It's not about paranoia, but about taking practical steps to secure your privacy. From your digital footprint to your physical surroundings, there are actionable steps you can take to safeguard your personal information.
Securing Your Digital Communications
Our digital lives generate a vast amount of data, making it a prime target for surveillance. One of the most effective ways to protect your online communications is using end-to-end encrypted messaging platforms. These platforms ensure only you and the intended recipient can read your messages. Signal and WhatsApp are two popular examples offering robust end-to-end encryption by default.
Regularly clearing your browsing history and using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can help mask your online activity, making it harder for others to track your movements. A VPN creates a secure, encrypted tunnel for your internet traffic, hiding your IP address and location. This is particularly useful when using public Wi-Fi.
Identifying Physical Surveillance: Spotting Hidden Devices
Detecting hidden cameras and microphones requires a keen eye and a methodical approach. Start by visually inspecting your surroundings. Look for anything out of place, such as unusual wiring, small holes in walls, or oddly positioned objects. Consider common hiding spots like smoke detectors, clocks, and electrical outlets.
You can also purchase bug detectors, which scan for radio frequencies emitted by hidden devices. These can be a useful tool for sweeping your environment.
Protecting Sensitive Conversations: Practical Tips
When discussing private matters, choose locations carefully. Avoid public places where conversations can be easily overheard. Consider the acoustics of a room; hard surfaces can reflect sound, making eavesdropping easier. Soft furnishings, on the other hand, can absorb sound.
For highly sensitive discussions, consider using white noise generators or playing background music to create audio interference. This can disrupt recording devices.
Managing Your Digital Footprint: Minimizing Tracking
Minimizing your digital footprint requires proactive steps to control the information you share online. Review your privacy settings on social media platforms and limit the personal information you make public. Be mindful of the apps you download and the permissions they request. Avoid granting access to your location, microphone, or camera unless absolutely necessary.
Remember, every click and search contributes to your digital footprint. By being proactive, you can make it harder for companies and individuals to track your online activities and collect data.
Seeking Professional Help and Understanding Your Legal Rights
If you suspect you are under unlawful covert surveillance, seek professional assistance. A qualified private investigator can conduct a thorough sweep of your premises to detect hidden devices and advise on counter-surveillance measures. Covert surveillance is regulated by law. If you have evidence of illegal surveillance against you, you have legal options.
The Regulation of Investigatory Powers Act 2000 (RIPA) governs surveillance practices in the UK. Understanding your rights under this legislation can help you determine whether surveillance against you has been lawful.
Concerned about your privacy? Sentry Private Investigators Ltd offers a range of services to protect you from unwanted surveillance. From bug sweeps and counter-surveillance measures to expert advice on legal remedies, we can provide the support you need. Contact us today for a confidential consultation.
Article created using [Outrank](https://outrank.so)



