People Tracing Guide: Methods, Services & Legal Tips
- Showix technical Team
- Jun 22, 2025
- 14 min read
Updated: Jul 28, 2025
What People Tracing Really Means (And Why It Matters)
When you hear the term people tracing, your mind might jump to cinematic scenes of private investigators on a stakeout or perhaps a quick search on social media to find an old school friend. While these scenarios touch upon the idea, professional people tracing is a much more systematic and detailed field. It's less about a single 'aha!' moment and more like assembling a complex puzzle, piece by piece, using verified information and methodical investigation.
Think of it this way: a casual online search is like skimming the contents page of a book. You get a general idea of the story but miss all the crucial details. Professional people tracing is like reading the entire book, understanding the characters, plot twists, and the author's intent. It involves a structured process of locating an individual for a legitimate purpose, ranging from deeply personal family reunions to critical legal and financial matters.

The screenshot above, from The National Archives, shows how foundational records like historical census data have long been used to connect people to specific places and times. These records are the bedrock of historical tracing, providing verifiable links that modern digital methods often build upon.
The Human Element of Finding People
The reasons behind a search are as varied as people themselves. A solicitor might need to locate the beneficiary of a will, who is unaware they are due an inheritance. A business may need to trace a former director for legal proceedings, or a lender could be searching for a debtor who has defaulted on payments. On a more personal level, an adopted adult might be on an emotional journey to find their birth parents, or a family could be desperate to reconnect with a relative lost to time and distance.
Each motivation shapes the entire investigative approach. For instance, the methods used by UK tracing agents to find a willing beneficiary will differ greatly from the discreet techniques required to serve legal documents to an individual who may be avoiding contact. This sensitivity and understanding of the context are what separate a professional service from a simple database search.
Verification Is the Cornerstone
At its core, people tracing relies on accurate and robust identity verification to ensure the right individual is being located and identified. Without this crucial step, the entire process can fall apart, leading to wasted time and effort, or worse, contacting the wrong person. This verification process has changed significantly over time.
Historically, tracing familial connections in the UK depended heavily on census records, which offer a rich source of demographic information from 1841 to 1921. These decennial records meticulously logged details like age, occupation, and household composition, creating an invaluable paper trail. You can explore the history and scope of these documents by reading the research guides on census records from The National Archives. Today, professionals combine these historical data points with modern, compliant databases to build a complete and accurate picture, ensuring every lead is validated before any conclusion is drawn.
How People Tracing Transformed From Parish Books To Digital
The idea of people tracing didn't just appear with the internet; its history goes back centuries, long before anyone had a digital footprint. The evolution from dusty parish books to the complex databases we use today mirrors major shifts in society and technology. In the past, finding someone was a local task, relying entirely on community records and word of mouth.
Picture trying to find a person in the 17th or 18th century. You wouldn't start with a search engine, but with a visit to the local church. Parish registers, which carefully documented baptisms, marriages, and burials, were the main source of information. These ledgers acted as the first databases, creating a paper trail of an individual's life within a specific town or village. This system worked well in an era when most people lived and died in the same small area.
The Rise of Systematic Record-Keeping
As society became more mobile, especially during the Industrial Revolution, these local methods started to fall short. People moved to cities for work, and a more centralised way of keeping track of them became essential. This need sparked the creation of national systems that completely changed how people tracing was done.
Civil Registration: The launch of civil registration in England and Wales in 1837 was a huge step forward. For the first time, births, marriages, and deaths were officially logged by the government, creating a single, nationwide index.
The Census: As noted earlier, the UK census, taken every ten years since 1841, offered a detailed look into every household. It became a priceless resource, allowing tracers to place a person in a specific location at a certain time, complete with family members and their occupation.
These systems formed the foundation of modern investigative work. They allowed professionals to follow a person's life through official documents in a structured way. Still, the work was slow and manual, often involving trips to archives and long hours looking through microfiche viewers.
The Digital Shift and Data Consolidation
The real game-changer was the arrival of computers. At first, technology simply digitised existing paper records, making them easier to search. But the internet took it a step further by connecting these separate datasets, weaving together a web of information that was once impossible to access. Electoral rolls, property records, company director details, and court documents were no longer locked away in physical buildings.
This change led to large-scale data aggregation. Government bodies started compiling huge datasets for research. A key example is the Office for National Statistics (ONS) Longitudinal Study, which began in 1974. This ongoing project links census data for more than 500,000 people, or about 1% of the population, providing a rich source for tracking demographic shifts over many years. You can find out more about this important study on the official ONS website.
Today, professional UK tracing agents work at the intersection of these historical methods and digital tools. They blend the methodical patience of traditional record-searching with the speed and scope of modern technology, using advanced algorithms to find links and confirm identities with a level of accuracy that was once unimaginable.
Professional People Tracing Techniques That Actually Work
Peeking behind the curtain of professional people tracing reveals a world where traditional investigative instincts meet powerful data analysis. It's far more than a simple online search; it's a systematic process that explains why professional services consistently get results where amateur attempts often come up short. Success relies on a multi-layered approach, combining digital forensics with real-world enquiries.
At the heart of modern tracing are specialised databases that aren't available to the general public. Experienced UK tracing agents subscribe to services that bring together vast amounts of information, including credit reference data, historical addresses from the electoral roll, and other commercial datasets. Think of it like having a master key that unlocks connections between millions of separate records. An agent might find a new address linked to an old mobile number or uncover a previously unknown associate through a shared financial product, carefully building a detailed picture of the subject's movements.
Blending Digital Trails with Human Intelligence
While databases provide the foundation, the real skill lies in interpreting the data and filling in the gaps. This is where digital investigation and human intelligence come together.
Social Media and Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT): Professionals go much deeper than a simple profile search. They analyse social networks, public forums, and online communities for clues. This could mean spotting a subject’s new workplace on a professional networking site or finding their location from geo-tagged photos posted by a friend. The key is to recognise patterns—piecing together seemingly random online activity to form a clear picture.
Field Enquiries: Sometimes, digital trails run cold. This is when strategic field enquiries become essential. This doesn’t mean dramatic stakeouts, but rather discreet, purposeful visits to last known addresses or local areas. Conversations with neighbours or local shopkeepers, handled ethically and professionally, can often provide the final piece of the puzzle that no database could.
Network Analysis: Often, the best way to find someone is through the people they know. Professionals map out the subject’s network of family, friends, and business associates. By discreetly approaching a contact on the periphery, they can sometimes get the crucial information needed to locate the subject directly. This process is detailed and requires careful handling, which you can read about in our guide on how tracing agents work.
This infographic shows the primary data sources professionals rely on for their investigations.
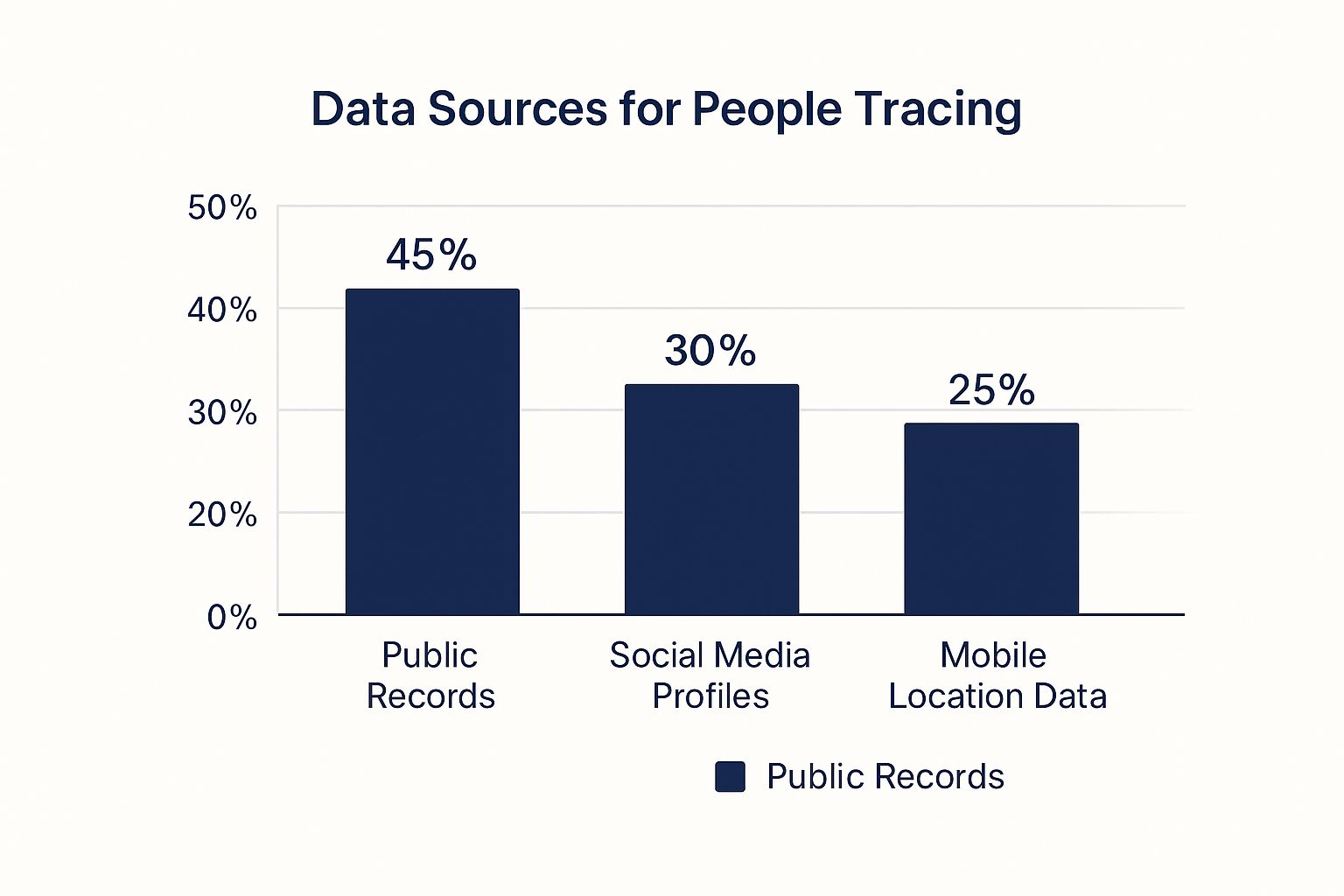
The chart highlights that while public records are the most significant source, social media and mobile data play a vital, complementary role in a modern trace.
The Influence of Other Disciplines
Interestingly, some effective people tracing techniques have roots in other fields. The structured approach used in public health for contact tracing, for example, shares similarities with professional investigative work. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the NHS Test and Trace programme showed the power of systematic tracing on a massive scale. In one week in August 2020, the system successfully reached 5,767 positive cases, with 75.9% of them providing details of their close contacts. This highlights the effectiveness of methodical, contact-based information gathering. You can explore more about this large-scale programme in the UK government's weekly reports. This systematic methodology—identifying a subject and then tracing their network outwards—is a principle that skilled tracers apply daily, just on a much smaller, more targeted scale.
Why People Need Tracing Services (Real Stories, Real Reasons)
Every request for a people tracing service starts with a human story. While the methods can be technical, the reasons behind them are deeply personal, spanning from heartfelt reunions to critical legal matters. Understanding these real-world motivations shows why professional help is often a vital step in solving complex problems. The context of a search determines the whole approach, influencing the tools, techniques, and level of discretion needed by skilled UK tracing agents.

Uncovering Family Connections
One of the most emotionally significant reasons for people tracing is reconnecting with family. These searches are often delicate and must be handled with great sensitivity.
Adoption Reunions: An adult who was adopted might want to find their birth parents. This search is about more than just finding a name; it's about understanding one's heritage and identity. The process involves carefully navigating adoption records and making initial contact with compassion.
Lost Relatives: Families can become separated due to disagreements, moving abroad, or simply losing touch over time. Someone might be searching for a long-lost sibling, a parent they no longer speak to, or a cousin they haven't seen since they were children. These cases often begin with faint memories and old photos, requiring a methodical search to bridge the gap of many years.
The Legal and Financial Imperative
Aside from personal journeys, a large number of people tracing cases are driven by legal and financial duties. In these situations, accuracy and speed are essential, as the results can have serious consequences. A solicitor, for instance, isn't just looking for a person; they are carrying out a legal responsibility.
Locating Beneficiaries: A common reason for tracing is to find heirs to an inheritance. It is not unusual for someone to pass away without up-to-date records of their beneficiaries' locations. Tracing agents are hired to find these individuals to ensure the deceased's final wishes are fulfilled.
Finding Witnesses: For legal cases to be fair, it's important that all key witnesses are heard. If a crucial witness has moved or cannot be found, it can put a case at risk. Tracers are brought in to locate these people so they can give their evidence.
Serving Legal Documents: Process serving is a core part of the justice system. It involves formally notifying someone that legal action is being taken against them. When a person actively avoids being served, a professional tracer is needed to find them and make sure the documents are delivered correctly, allowing the legal process to continue.
Debtor and Tenant Tracing: Businesses and landlords often find themselves in situations where a debtor or former tenant has vanished, leaving unpaid bills or property damage. Tracing these individuals to a new address is the first and most important step in recovering money owed through legal means.
To give a clearer picture of why people use these services, the table below shows a breakdown of common requests and their typical outcomes.
Most Common People Tracing Requests
Statistical breakdown of the most frequent reasons people seek tracing services and their typical outcomes
Reason for Tracing | Percentage of Cases | Average Success Rate | Typical Complexity Level |
|---|---|---|---|
Debt Recovery | 40% | 90-95% | Low to Medium |
Family Reunification | 25% | 75-85% | High |
Locating Beneficiaries | 20% | 85-90% | Medium to High |
Process Serving | 15% | 95%+ | Low to Medium |
As the data shows, while debt-related searches are the most frequent, more emotionally driven searches like family reunions make up a significant portion of cases, though they often present greater challenges.
Legal Boundaries In People Tracing (What You Must Know)
While the methods of people tracing are powerful, they operate within a strict legal framework designed to protect individual privacy. Navigating this area requires more than just technical skill; it demands a solid understanding of what is allowed and what crosses a serious legal line. Think of it like driving a high-performance car: you have the power to go fast, but you must still obey the rules of the road—speed limits, traffic signals, and right of way—to ensure everyone’s safety.
For anyone involved in people tracing, from solicitors to private individuals, these rules are not optional. The main legislation governing the use of personal data in the UK is the Data Protection Act 2018, which works in tandem with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). These laws establish clear principles for how personal information can be collected, used, and stored.
GDPR and the Lawful Basis for Tracing
At the core of any compliant people tracing activity is the concept of a "lawful basis for processing." This means you can't simply search for someone out of curiosity. Professional UK tracing agents must first establish a legitimate, legally recognised reason to begin a search. These bases include:
Legitimate Interests: This is the most frequent basis used for tracing debtors or beneficiaries of a will. The company or individual has a valid interest in recovering owed money or fulfilling the terms of an estate, and tracing is necessary to do so.
Legal Obligation: Often, legal firms have a duty to locate individuals, for example, to serve court documents or notify them of legal proceedings.
Consent: In some situations, like a family reunion search, consent might be the appropriate basis. However, this can be complicated, as the person being sought cannot give their consent until after they have been found.
A vital part of respecting these legal boundaries is maintaining robust data privacy compliance standards. Any professional service must be able to show that its methods are necessary, proportionate, and respect the rights of the individual. This means only accessing the information that is absolutely required and not gathering excessive data. For instance, finding a current address to serve a legal notice is acceptable, but accessing private medical records would be a severe violation.
The Line Between Investigation and Harassment
This is where the difference between professional tracing and unacceptable behaviour becomes incredibly clear. A legitimate investigation is focused on finding a person for a lawful reason. The process is methodical, discreet, and respectful. Actions that cross into harassment or stalking are illegal and can include:
Repeatedly contacting the person after they have asked to be left alone.
Publishing private information about them.
Monitoring their movements in a way that causes fear or alarm.
Professional tracers have strict protocols for when a person explicitly states they do not wish to be found. In many personal cases, such as a family search, the agent's duty is to pass on a message and then respect the individual's decision, acting as a neutral intermediary. Their role is to locate, not to force a confrontation. This ethical code is central to how reputable agencies operate, ensuring the process remains lawful and respectful from beginning to end.
Choosing Professional People Tracing Services That Deliver
Choosing a partner for a people tracing assignment is a significant decision. Not all services offer the same level of quality, and your choice could mean the difference between finding the person you're looking for and wasting time and money. Think of it like hiring a skilled jeweller versus a general repair person; both might have tools, but only the expert has the precise knowledge for a delicate and important task. A professional service brings deep expertise, legal know-how, and a proven track record.

Key Credentials to Verify
Before you hire any service, it’s vital to do your homework. A credible agency will be open about its credentials and how it works. Start by checking for these essential signs of professionalism:
Information Commissioner's Office (ICO) Registration: In the UK, any organisation handling personal data is legally required to be registered with the ICO. This is a fundamental requirement. You can verify their registration number on the official ICO public register.
Professional Memberships: Look for affiliations with respected industry bodies, such as the Association of British Investigators (ABI). Membership shows a commitment to high professional standards and a strict code of ethics.
Insurance: A legitimate agency must have professional indemnity and public liability insurance. This protects both you and them if any errors or legal issues arise.
Clear Pricing Structure: Be wary of vague or suspiciously cheap pricing, as it can be a major red flag. A professional firm will give you a clear, upfront quote that details all possible costs. Be cautious of "no find, no fee" deals that sound too good to be true, as they often lead to cut corners or reliance on poor-quality data.
Questions to Ask a Potential Provider
Once you have a shortlist of agencies, treat your first conversation like an interview. Their answers will tell you a lot about their experience and methods. Be ready to ask specific questions:
What is your success rate for cases similar to mine?
Can you explain your lawful basis for processing data under GDPR for this search?
What is your procedure if the person found says they do not wish to be contacted?
Will I receive a detailed report of your findings?
The answers you get should be confident, clear, and based on solid legal and ethical practices. If an agent seems hesitant to discuss their methods or promises a 100% success rate, it's wise to look elsewhere. The truth is that some individuals are extremely difficult to locate, and no honest professional can promise a guaranteed result every single time. For more advice on picking the right provider, our guide on the best UK tracing agents offers additional helpful tips.
In the end, selecting the right service is about finding a provider that combines skill with transparency and ethical conduct. A dependable agency knows how sensitive this work is and will operate with discretion and integrity, making sure your search is not only successful but also handled respectfully and in full compliance with the law.
DIY People Tracing: What You Can Accomplish Yourself
While professional services often have higher success rates, trying a preliminary search on your own can be a great first step. Before calling in the experts, there are several practical people tracing methods you can use to gather some initial information. Think of it like doing your own prep work before a decorator arrives; the groundwork you lay can make the final job much smoother and more successful.
A sensible place to begin is with a standard internet search. Using search engines effectively is about more than just typing in a name. Try putting quotation marks around a full name to search for that exact phrase. You can also add details like a last known town or profession to help narrow down the results.
Online Resources and Public Records
The internet has made a vast amount of information accessible right from your own home. These resources can give you the foundational clues needed for your search:
Social Media Platforms: Look beyond the big names. Consider specialised networks for hobbies, professions, or old school friends. People often share details about their lives and locations without giving it a second thought.
Genealogy Websites: Services like Ancestry or Findmypast are brilliant resources. They offer access to census data, birth records, and family trees that can help you piece together someone's history and find potential living relatives.
Public Records: The electoral roll, which you can check at local council offices or libraries, can confirm an address. Many local authorities also have searchable online databases for things like planning applications, which can provide clues.
For those keen on exploring these self-service options, a guide on how to track social media mentions can offer useful techniques for gathering information online.
Recognising the Limits
It’s important to understand that DIY people tracing requires a lot of time and emotional resilience. The process can be very slow, and hitting a dead end is not only common but can also be quite disheartening. Also, while many online searches are free, accessing detailed records on genealogy sites or ordering official certificates involves costs that can quickly add up.
You need to know when you've reached the end of what you can do by yourself. If your search involves tricky circumstances, a person who might not want to be found, or if you simply run out of leads, it's time to think about professional help. Skilled UK tracing agents have access to specialised databases and investigation methods that aren't available to the general public. If you're struggling with a search that involves a phone number, you might find our article on UK phone number tracing methods useful.
When you've exhausted your options, bringing in a professional isn't admitting defeat—it's taking the next logical step towards finding a solution. Sentry Private Investigators Ltd combines expertise with discretion to handle even the most difficult cases. Contact us today to see how we can help you find the answers you're looking for.




